LMS-SPADA INDONESIA
LMS-SPADA INDONESIA
Course Content
Topic outline
-

-
About this chapter
Welcome to the Database Class!
In our first class, we will be looking at the new perspectives, which is the perspective of data, more specifically, database system.
We are surrounded by data, students data, customer data, library's book data, and many more.
Start by understanding the need for understanding what is data and data management.
Learning Objectives:- Understanding the real daily life examples of database application.
- Understanding between the file-based and database system.
- The DDL and DML as the database approach.
- Components, advantages and disadvantages of DBMS.
- Features of three-level architecture.
- Importance of data independence
- Data model (relational. network, hierarchical)
Learning Structures:
This chapter consists of
1. Reading materials
2. Video materials
3. Discussions -
Pre Learning Activities
-
Main Learning Activities
The main learning activities surround the discussions of common uses of the database systems, the meaning of the term database and the meaning of the term Database Management System (DBMS).
The student is advised to consults for the pre-class materials and the main learning activities.You need to have a Miro account. Please create one if you do not have it. Join here once you login to your Miro account. -
Post Learning Activities
-
-

-
About this chapter
Welcome to the second class of Database Systems!
Continuing the excitement from the previous lesson, this chapter will continue the discussion of Database Management System. The discussion on Three-Layer architecture promises logical and physical data independence, thus user External View protected from lower level changes.
Here, we will see how the DBMS able to perform functionality from different users, through Query, DML and DDL process. Further, we will see different approaches of users, such as the types Administrator, Naive vs Sophisticated user, and Application Programmer. As your post-material, a quiz is given afterwards. Stay focused, and lets roll the chapter 2, DBMS.
Learning Objectives:
- Components of a DBMS
- Components of Database Manager
- The architecture of multi-users DBMS architecture (teleprocessing, fileserver, and client-server)
- Tier of Client-Server
- Transaction Processing Monitors
- Cloud Model
- Conceptual data model
- Mini world scenarios
- Characteristics of database approached (data abstractions, multiview, sharing data)
- Database schema vs database state.
Learning Structures:
- Reading materials
- Video materials
- Discussions
- Quiz
-
Pre-learning Activities -
Main Learning ActivitiesClick this to join with the class session. You need a Miro account in order to join.
-
Post Activity MaterialsStudent is need to prepare on the conceptual (high-level) information to a simple Mini-World case, which is the conceptual model of university’s database that enable student to access to their grades and transcripts at a university.
Student need to show the ability to think logically on the need of the user and the required database Entity to full fill the user request.
-
-

-
About this chapterWelcome to the third module of Database System.
In this chapter, students will be introduced with the new function and terminology of the Database System, which are Relation and Keys.
As the Entity of the Database has set in the mini-world example, the relational model between entity table and the connection between them through keys will be further explored.
Learning Objectives
- Terminology of relational model.
- How tables are used to represent data.
- Connection between mathematical relations and relations in the relational model.
- Properties of database relations.
- How to identify CK, PK, and FKs.
- Meaning of entity integrity and referential integrity.
- Purpose and advantages of views.
Learning Structures:
This chapter consists of- Reading materials
- Video materials
- Discussions
-
Pre-learning ActivitiesDatabase as the vital aspect / component of an enterprise / an organization are build based on layered of establishment.
Started as Conceptual (high-level, semantic) data models, Physical (low-level, internal) data models, and finally reached to Implementation (representational) data models:
Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter 2 and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity.
-
Main Class ActivityThis chapter comprises of the discussion of Database Design Process, along with the ER Model Concepts: Entities, attributes, relationships. As the real-life example for the Database design process, a generic example is used (such as Company, Product (car) and University).
This chapter also look at the Constraints and Cardinality in the ER model, which focuses more on the activities of Database design on the conceptual schema of the database design.
-
-
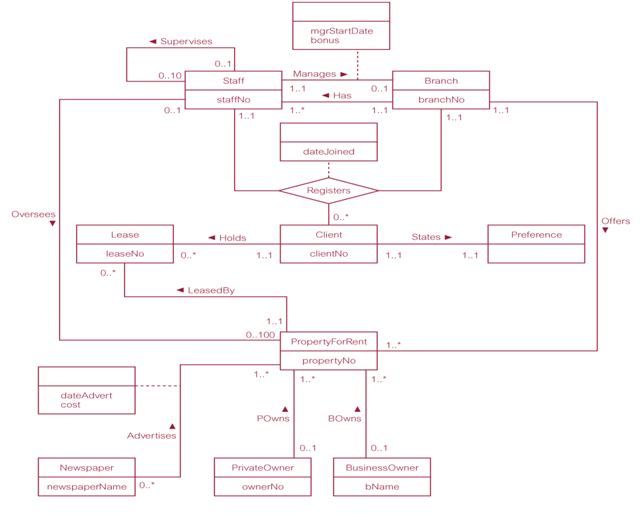
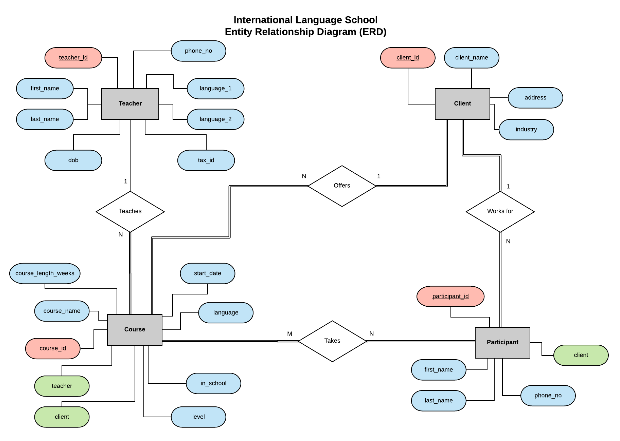
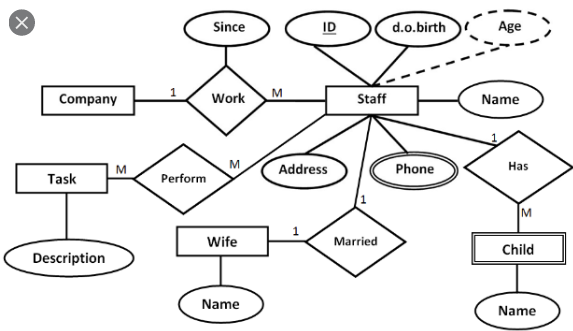
About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about data modeling. A data modeling is the first step of a database design. A good data modeling will help the database designer to create a proper database that matches to both the user's needs and the system's requirements.
Entity Relational Diagram (ERD) will be used as a tool of database modeling. A well-designed ERD shows a complete users (entity) interaction with the database.
Learning Objectives:
- How to use Entity–Relationship (ER) modeling in database design.
- Basic concepts associated with ER model.
- Diagrammatic technique for displaying ER model using Unified Modeling Language (UML)
- How to identify and resolve problems with ER models called connection traps.
- How to build an ER model from a requirements specification.
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online collaboration for Entity Relationship Diagram practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-

About this chapter
In this part you will create a database modeling based on the case given in this section.
Learning Objectives:
- How to use Entity–Relationship (ER) modeling in database design.
This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online collaboration for Entity Relationship Diagram practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1 hours
- Watching Videos: 10 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Online workshop: 1,5 hours
- Group Assignment: case study presentation
- How to use Entity–Relationship (ER) modeling in database design.
-

-
Instruction
- Read the following cases below.There are two cases. You are required to provide database design to support the business process given in the case.
- Student whose last digit of his/her ID is Odd (ganjil) work only Case 1. While student whose last digit of his/her ID is even (genap) or 0 will work on Case 2.
- Design a database to support all general business processes. A bonus business process is not a must, but it will give you extra score if you do it correctly.
- Use Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) to create the database modeling.
- Use any tools to draw the ERD, and capture the diagram and copy it to Microsoft Excel.
- Convert the ERD into tables the represent the database. Create those tables in the same Microsoft Excel file.
- Insert or provide data, min 5 record per table.
- Test the tables. Make sure they are normal.
- Upload and submit the Microsoft Excel file in your course in eCampus. The file must consist of ERD and tables including the data sample.
Case 1:
A restaurant is developing a new information system. The system needs a database to support the business process in the restaurant.Below are the business processes:
- Customer must be registered as member of the restaurant.
- Customer choose menu via offline. The customer needs to go to the restaurant to choose the menu.
- There are two payment methods: Cash or Credit/Debit Card.
- There are several types of menu. For example: meal, drinks, snack, etc.
- Customer received bill that contains detail of item purchased (name, quantity), total payment, payment methods, customer name, and transaction date.
Bonus:
Some menu may have discount. The discount is based on menu package. For example, IF customer buy Package A (2 nasi goreng, 2 tea, 2 ice cream) THEN the total price will get 5% discount. The package is cheaper rather than they buy the menu not in a package.
Case 2
A motorcycle repair shop (bengkel motor) is developing a new information system. The system needs a database to support their business process.
The business process are as followed:- Customer must be registered as member of the motorcycle repair shop.
- Customer must book a schedule for motorcycle service. The book record: customer name, type of motorcycle, motorcycle number (nomor polisi), date, and note. Note can be filled with customer's complain about his/her motorcycle.
- After the service, the customer will receive the bill that
contains of the book number (book ID), list of services (i.e clean the
engine, check the engine, etc), list of product (lubricant, any
sparparts, etc.), price of each services, price of each product, total
payment, date.
Bonus:
There are 3 level of membership, Gold, Silver, and Bronze. Each level will give different discount. For example Gold member will have 20% discount of service, Silve will have 15% and Bronze will have 10%. - Read the following cases below.There are two cases. You are required to provide database design to support the business process given in the case.
-
-

About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about MS. SQL Server Express edition that can easily be downloaded from the vendor's website. After installation we will continue to see some features in MS. SQL Server.
MS SQL Server is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. This product is built for the basic function of storing retrieving data as required by other applications. It can be run either on the same computer or on another across a network
Learning Objectives:
- How to install MS. SQL Server Express Edition .
- Login and set permission.
-
Create database, tables
- Define Primary Key, Foreign Key
- Show relationship between table
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session and practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
Microsoft SQL Server is an application used to create computer databases for the Microsoft Windows family of server operating systems. Microsoft SQL Server provides an environment used to generate databases that can be accessed from workstations, the Internet, or other media

Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about introduction to Ms. SQL Server
-
In this main learning activities, we would like to invite you to install and walkthrough on MS. SQL Server.
 During the online session, we expect you to engage with the learning activities especially on how install and use MS. SQL Server by following the step by step instruction from the lecturer.
During the online session, we expect you to engage with the learning activities especially on how install and use MS. SQL Server by following the step by step instruction from the lecturer. -
After you have install and learned MS. SQL Server, as well as learn the step-by-step to install and use it, now you need to start creating your own business database.There is an individual assignment in this post learning section. Read the instruction about the assignment carefully. You are required to create a database for your own business
-
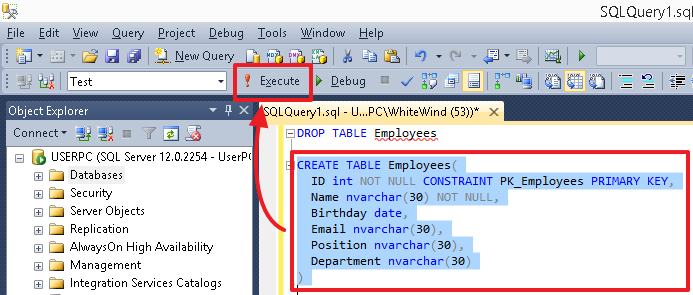
About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about how to create database, tables and inputting data by using SQL syntax.
Learning Objectives:
- How to create database and tables by using query syntax .
- How to create the relationship between tables
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
A table is a collection of related data held in a table format within a database. It consists of columns and rows. In relational databases, and flat file databases, a table is a set of data elements (values) using a model of vertical columns (identifiable by name) and horizontal rows, the cell being the unit where a row and column intersect. A table has a specified number of columns, but can have any number of rows. Each row is identified by one or more values appearing in a particular column subset. A specific choice of columns which uniquely identify rows is called the primary key.
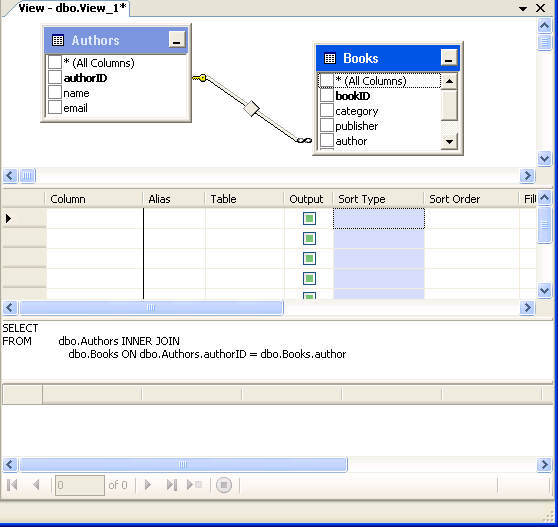
Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about managing tables in MS. SQL Server
-
In this main learning activities, we would like to invite you to practice about creating database, tables and relationship on MS. SQL Server.
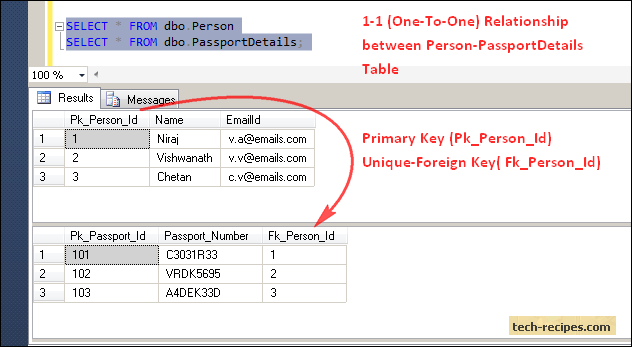 During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer
During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer -
After you have followed all the instruction during the class, your are asked to create your own database, tables and relationship between those tables.There is an individual assignment in this post learning section. Read the instruction about the assignment carefully. You are required to create a complete database (tables, relationship) for your own business
-

About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about how to do data manipulation language (DML) by using SQL syntax.
Learning Objectives:
- How to INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE by using query syntax .
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
A data manipulation language (DML) is a computer programming language used for adding (inserting), deleting, and modifying (updating) data in a database. A DML is often a sublanguage of a broader database language such as SQL, with the DML comprising some of the operators in the language. Read-only selecting of data is sometimes distinguished as being part of a separate data query language (DQL), but it is closely related and sometimes also considered a component of a DML; some operators may perform both selecting (reading) and writing. A popular data manipulation language is that of Structured Query Language (SQL), which is used to retrieve and manipulate data in a relational database.

Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about data manipulation in MS. SQL Server
-
In this main learning activities, we would like to invite you to practice about how to INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE tables on MS. SQL Server.
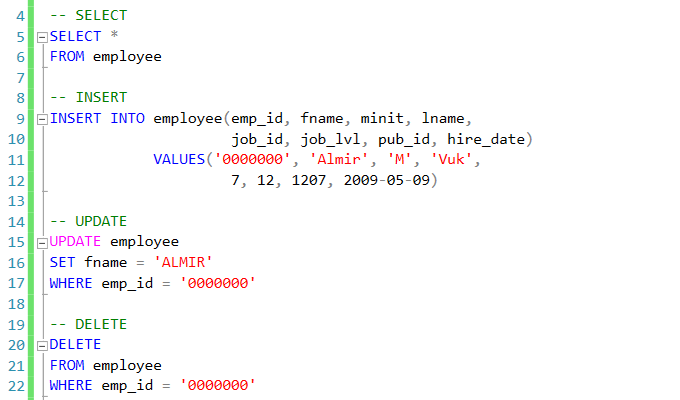 During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer
During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer -
After you have followed all the instruction during the class, your are asked to manipulate some tables on your previous database. There is an individual assignment in this post learning section. Read the instruction about the assignment carefully. You are required to modified your previous database
-

About this chapter
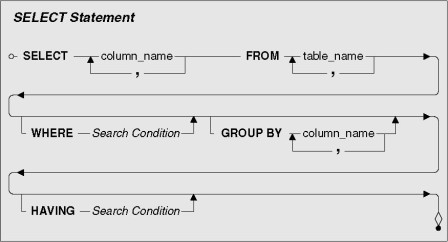
In this chapter, we will learn about retrieving data from tables by using SQL syntax. The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records, from one or more tables. A SELECT statement retrieves zero or more rows from one or more database tables or database views. In most applications, SELECT is the most commonly used data manipulation language (DML) command
Learning Objectives:
- Purpose and importance of SQL.
- How to retrieve data from database using SELECT
- Use compound WHERE conditions.
- Sort query results using ORDER BY.
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session and practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
DDL(Data Definition Language) : DDL or Data Definition Language actually consists of the SQL commands that can be used to define the database schema. It simply deals with descriptions of the database schema and is used to create and modify the structure of database objects in the database.
Examples of DDL commands:
- CREATE – is used to create the database or its objects (like table, index, function, views, store procedure and triggers).
- DROP – is used to delete objects from the database.
- ALTER-is used to alter the structure of the database.
- TRUNCATE–is used to remove all records from a table, including all spaces allocated for the records are removed.
- COMMENT –is used to add comments to the data dictionary.
- RENAME –is used to rename an object existing in the database.
Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about data manipulation in MS. SQL Server
-
In this main learning activities, we would like to invite you to practice about how to retrieve data from database using SELECT on MS. SQL Server.
 During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer
During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer -
After you have followed all the instruction during the class, your are asked to retrieve some tables on your previous database. There is an individual assignment in this post learning section. Read the instruction about the assignment carefully. You are required to modified your previous database
- Purpose and importance of SQL.
-
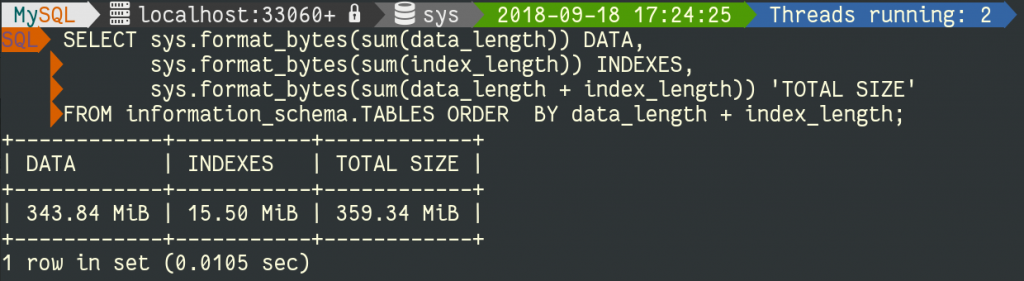
About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about retrieving data from tables by using SQL syntax. The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records, from one or more tables. A SELECT statement retrieves zero or more rows from one or more database tables or database views. In most applications, SELECT is the most commonly used data manipulation language (DML) command
Learning Objectives:
- Use aggregate functions.
- Group data using GROUP BY and HAVING.
- Use subqueries.
- Join tables together.
- Perform set operations (UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT).
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session and practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
An aggregate function performs a calculation on a set of values, and returns a single value. Except for COUNT(*), aggregate functions ignore null values. Aggregate functions are often used with the GROUP BY clause of the SELECT statement. All aggregate functions are deterministic. In other words, aggregate functions return the same value each time that they are called, when called with a specific set of input values. See Deterministic and Nondeterministic Functions for more information about function determinism. The OVER clause may follow all aggregate functions, except the STRING_AGG, GROUPING or GROUPING_ID functions.
Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about data manipulation in MS. SQL Server
-
In this main learning activities, we would like to invite you to practice about how to retrieve data from database using SELECT on MS. SQL Server.
 During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer
During the online session, we expect you to use laptop and follow step by step instruction from lecturer
- Use aggregate functions.
-
About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them by using SQL syntax. An SQL join clause – corresponding to a join operation in relational algebra – combines columns from one or more tables in a relational database. It creates a set that can be saved as a table or used as it is. A JOIN is a means for combining columns from one (self-join) or more tables by using values common to each.
Learning Objectives:
- Data types supported by SQL standard.
- Purpose of integrity enhancement feature of SQL.
- How to define integrity constraints using SQL.
- How to use the integrity enhancement feature in the CREATE and ALTER TABLE statements.
- Purpose of views.
- How to create and delete views using SQL.
- How the DBMS performs operations on views.
- Under what conditions views are updatable.
- Advantages and disadvantages of views.
- How the ISO transaction model works.
- How to use the GRANT and REVOKE statements as a level of security.
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session and practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
A
JOINis a means for combining columns from one (self-join) or more tables by using values common to each. ANSI-standard SQL specifies five types ofJOIN:INNER,LEFT OUTER,RIGHT OUTER,FULL OUTERandCROSS. As a special case, a table (base table, view, or joined table) canJOINto itself in a self-Join.A programmer declares a
JOINstatement to identify rows for joining. If the evaluated predicate is true, the combined row is then produced in the expected format, a row set or a temporary table.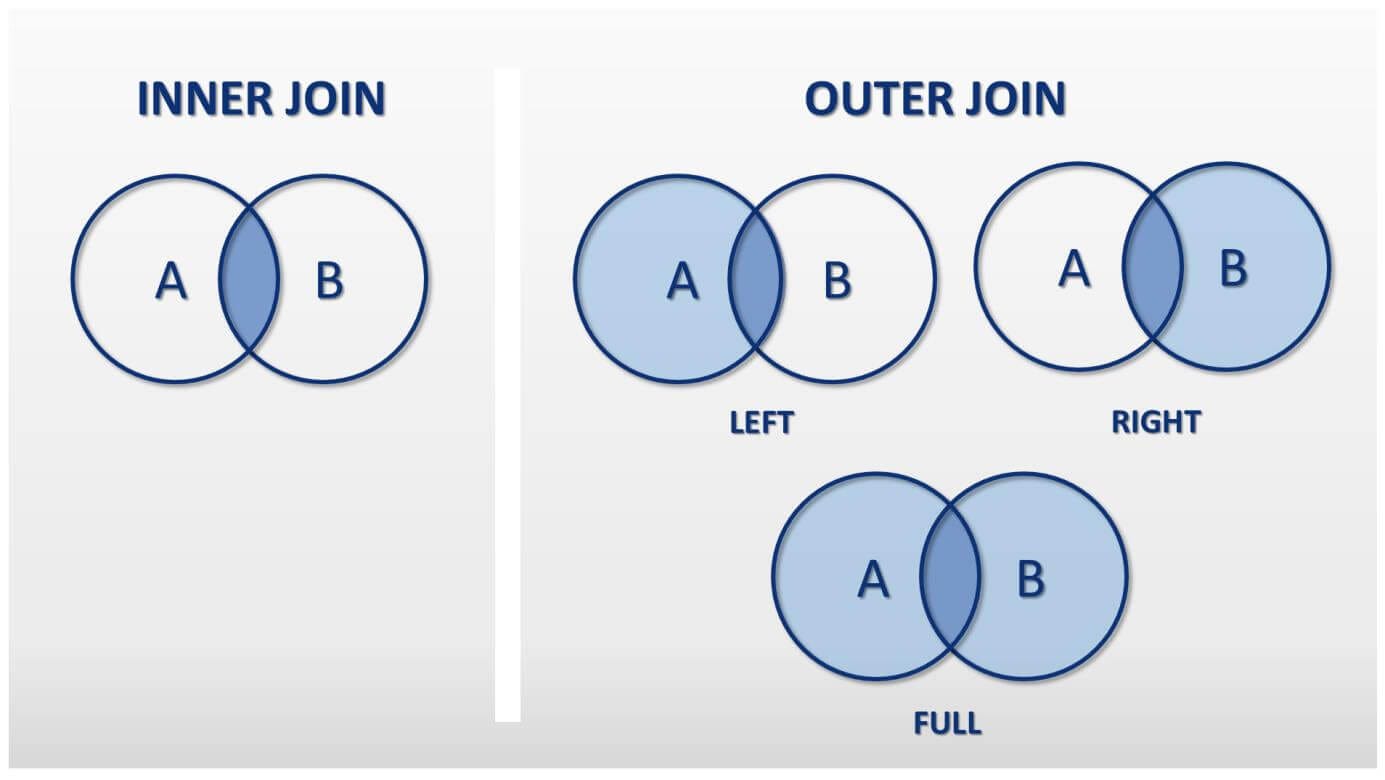
Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about data manipulation in MS. SQL Server
-
In this main learning activities, we would like to invite you to practice about how to retrieve data from database using SELECT JOIN syntax on MS. SQL Server.

Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about data manipulation in MS. SQL Server
- Data types supported by SQL standard.
-
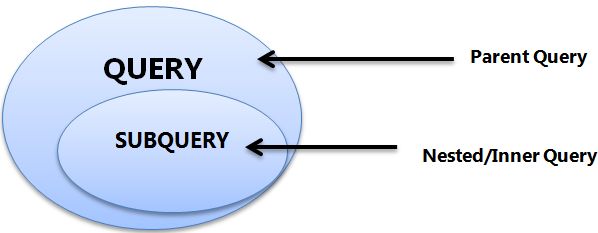
About this chapter
In this chapter, we will learn about retrieving data from tables by using sub query syntax. After that, we will also learn about advance SQL, that is Store procedure and trigger
Learning Objectives:
- How to use the SQL programming language
- How to use SQL cursors
- How to create stored procedures
- How to create triggers
- How to use triggers to enforce integrity constraints
- The advantages and disadvantages of triggers
- How to use recursive queries
Learning Structure:This chapter consists of reading material, lecturer-presentation material, and some videos. You need to read and watch the materials prior to the class session. In the main activity (class session), we would like to invite you with the online class session and practices. In the end of this chapter, there is an assignment that you need to accomplish. Here is the structure of learning activities:- Reading text book: 1,5 hours
- Watching Videos: 15 minutes
- Online collaboration: 2 hours
- Individual Assignment: 1 individual project (duration: 1 week)
-
A subquery is also called an inner query or inner select, while the statement containing a subquery is also called an outer query or outer select. A subquery is a query that is nested inside aSELECT,INSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEstatement, or inside another subquery.SQL Server stored procedure is a batch of statements grouped as a logical unit and stored in the database. The stored procedure accepts the parameters and executes the T-SQL statements in the procedure, returns the result set if any. A trigger is a special type of stored procedure that automatically runs when an event occurs in the database server. DML triggers run when a user tries to modify data through a data manipulation language (DML) event.

Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about data manipulation in MS. SQL Server
-
In this section, we would like to invite you to practice about how to retrieve data from database using Subquery, create Store procedure and Trigger on MS. SQL Server.
Student required to take and understand the post-activity of the previous Chapter and complete the reading required prior the Main class activity. Read the following lecturer presentation notes before we start with the class session. You may also need to watch the video about Advanced SQL (how to create Store procedure and Trigger)
- How to use the SQL programming language
-

-
This is an online (synchronous) exam. Join with the online session via link given to you. You are required to present the database modeling and demo the queries on some relevant reports. The database must be designed based on the case given by the lecturer during the exam.
-
-

-
View Submit feedback
Dear Students. Thanks for participating in this course. We hope that you can learn more from this course and make it relevant to your study.
Before completing this course, we would be please if you put some comments and inputs for our improvement. Please feel free to fill in this online feedback.
Thanks
Database System Online Course Team
-